Fisherman's Guide To The Microbiome: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== The Ecosystem == | == The Ecosystem == | ||
First a brief and factual description of the ecosystem our microbiome is... | |||
According to Harvard Health Online: | According to Harvard Health Online: | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
== Visualize == | == Visualize == | ||
Now let's consider a line drawing of me and my gut. It's just an empty pipe. | |||
[[File:meandmygut.jpg]] | [[File:meandmygut.jpg]] | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
The most important thing to get out of this visual exercise is that you have a living ecosystem in your gut. I think this will help people think of their microbiome as something that needs to be considered, taken care of and nurtured. | The most important thing to get out of this visual exercise is that you have a living ecosystem in your gut. I think this will help people think of their microbiome as something that needs to be considered, taken care of and nurtured. | ||
== | == The Landscape == | ||
Next let's visualize the landscape. | |||
== dd == | == dd == | ||
Revision as of 18:25, 22 February 2022
Congratulations!!! The fact that you are reading this webpage means you have made enough of a connection between your health and your microbiome to be here. Making that connection is a great place to start and hopefully the information in this wiki will help you further understand that relationship.
I am not a fisherman but I do have a useful understanding of how my microbiome works that I equate with fishing. Fishing techniques range from science based as commercial fishing operations are likely to utilize to the fuzzy logic traditional, low-tech artisanal fisherman use based on observations in the field.
This Fisherman's Guide To The Microbiome is at the low-tech end of the scale. It is something anyone can read and understand using just plain common sense.
The Ecosystem
First a brief and factual description of the ecosystem our microbiome is...
According to Harvard Health Online:
- About 100 trillion bacteria, both good and bad, live inside your digestive system. Collectively, they're known as the gut microbiota.
In the Encyclopedia of Cell Biology:
- The gut microbiome is the collection of microorganisms including bacteria, archaea, viruses, and fungi found within the gut and their overall genetic information. Our gut microbiota has been shown to have broad effects on our health and well-being, impacting our immune system and metabolism, detoxifying various ingested components, and even affecting behavior.
Well put! The Fisherman says that sounds right.
This phrase is very important in the context of the type of Failure Of TGA that I describe in detail in this wiki:
- detoxifying various ingested components
The Fisherman says that "various ingested components" means chemical compounds in our food. And "detoxifying" means taking care of the chemical compounds in our food that we are not designed to handle. So in this sense our microbiome acts like the garbage collector. In fact it's a symbiotic relationship: we have something we don't need and don't know what to do with but our microbiome has a use for it and disposes of it.
In terms of the numbers of bacterial species, kind of like teams or families, I have read estimates ranging from 400 to a few thousand. My guess based on what I see on the Internet it is a few 1000 but science so far only understands some of them and are therefore recognizing a few hundred as consequential.
Mixed in with our bacterial microbiome is our virome, a collection of viruses that also inhabit our gut. It is estimated there are 140,000 different viruses living there. Unfortunately even less is known about our virome than our microbiome.
For our purposes it is adequate to understand that at our level of operation we are talking about species and strains of bacteria, strains are a subset of species. For an in depth explanation of bacterial taxonomy please check out:
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bacterial_taxonomy
For further research:
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_microbiome
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virome
Enough numbers and science, suffice to say there are a lot of microbes in us and they have a consequential impact on our health.
Visualize
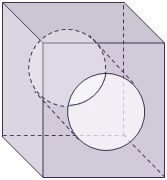
Now let's consider a line drawing of me and my gut. It's just an empty pipe.
While I think of my gut as my insides it's not. It's the outside running through me. In the context of conventional medicine treating my microbiome, this picture illustrates the problem, it's a jurisdictional issue: doctors treat me, that includes all parts of my body in the cube, it doesn't include the outside, that is my jurisdiction and responsibility.
But doctors do require access to my gut though for the administration of medicine. Under this arrangement any microbiome dysbiosis caused by the prescribed medication is my responsibility to monitor and repair. That's not right, this needs to change. I'm not equipped to be able to do that. At a minimum a patient needs to understand what expected impact a medicine will have on their microbiome.
Now let's imagine the ecosystem that inhabits this pipe that runs through me. Not a literal image but an imaginary one. Personally I think of my microbiome as a river full of fish, bugs, plants, snakes. The idea of a meandering river lends itself to the imagination of my microbiome but other schemes could work too. Maybe a factory or even Pokemon characters.
The most important thing to get out of this visual exercise is that you have a living ecosystem in your gut. I think this will help people think of their microbiome as something that needs to be considered, taken care of and nurtured.
The Landscape
Next let's visualize the landscape.